E-governance, moreover known as electronic governance, may be a worldview move within the way governments connected with citizens and convey open administrations. With the quick headway of digital technologies, governments around the world are grasping e-governance as a implies to progress proficiency, straightforwardness, and openness. This article investigates the concept of e-governance, its benefits, challenges, and its affect on open organization within the advanced age.
Understanding E-Governance
E-governance alludes to the utilize of information and communication innovations (ICTs) to change over the way governments connected with citizens, businesses, and other government substances. It encompasses the digitization of government shapes, administrations, and insights, making them more capable, straightforward, and citizen-centric.
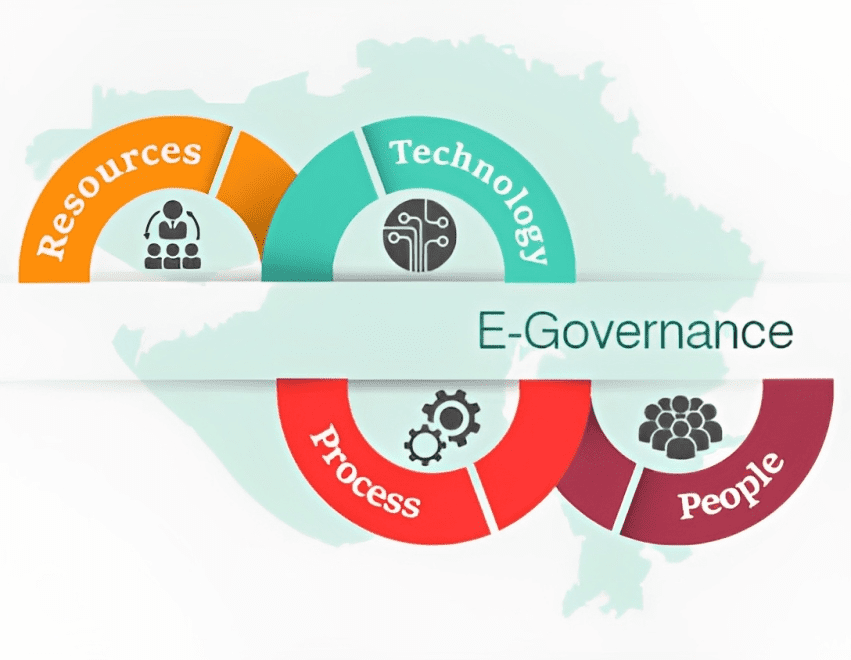
Key Components of E-Governance
E-governance comprises several key components that work together to enhance public administration:
Robust and secure computerized foundation, including broadband systems, data centers, and secure communication channels, forms the foundation for e-governance initiatives.
Online platforms and entrances empower citizens to get to government services, such as applying for permits, paying taxes, and obtaining official documents, conveniently and securely from anywhere, anytime.
Establishing secure digital identity systems, such as digital signatures and biometric authentication, enhances the trust and security of e-governance transactions.
Data Integration and Interoperability:
Integration of data over various government departments and systems encourages seamless data trade, reducing duplication of efforts and enhancing service delivery.
Making government data open to the public in a machine-readable format promotes transparency, enables data-driven decision-making, and encourages innovation.
Benefits of E-Governance
E-governance offers a wide range of benefits for both governments and citizens:
Enhanced Benefit Conveyance:
E-governance streamlines administrative processes, reducing bureaucratic delays and improving the productivity of benefit conveyance. Citizens can get to administrations online, saving time and effort.
Transparency and Responsibility:
Computerized stages give greater straightforwardness, enabling citizens to monitor government activities, get to data, and participate in decision-making forms. It too facilitates the discovery of corruption and promotes accountability.
Cost Effectiveness:
E-governance optimizes resource utilization by reducing paperwork, manual forms, and the need
for physical infrastructure. This leads to cost savings for governments and taxpayers.
Citizen Empowerment:
E-governance empowers citizens by giving them easy access to government information and services. It promotes inclusivity and enables citizens to actively lock in in governance processes.
Improved Decision-Making:
Information analytics and visualization tools enable policymakers to form informed choices based on real-time insights, leading to more effective and evidence-based governance.
E-Governance Challenges
Implementing e-governance initiatives comes with its claim set of challenges:
Digital Partition:
Unequal to advanced infrastructure and web connectivity makes a digital separate, restricting the reach of e-governance activities. Governments need to ensure inclusivity and bridge this gap.
Cybersecurity and Security:
With increased digital interactions, protecting sensitive information and guaranteeing security gotten to be basic. Governments must invest in robust cybersecurity measures and set up solid data protection frameworks.
Change Administration:
Shifting from traditional administrative processes to e-governance requires alter management efforts, including training programs, capacity building, and stakeholder engagement.
Legal and Administrative Frameworks:
E-governance activities need supportive lawful and regulatory systems to ensure compliance, protect citizens’ rights, and oversee digital transactions.
Implementing E-Governance Initiatives:
Successful implementation of e-governance initiatives requires careful planning and execution:
Vision and Procedure:
Governments should create a clear vision for e-governance and define a comprehensive strategy to align with their administrative goals and citizen expectations.
Infrastructure Advancement:
Contributing in advanced foundation, counting web network, information centers, and secure communication channels, is significant to back e-governance initiatives.
Partnerships and Collaboration:
Governments can collaborate with private segment substances, the scholarly world, and respectful society organizations to use skill, assets, and development for effective e-governance implementation.
Citizen Engagement:
Including citizens in the plan, implementation, and evaluation of e-governance initiatives fosters possession, trust, and usability.
Continuous Assessment and Change:
Standard assessment and input mechanisms help recognize regions for enhancement and ensure the viability and efficiency of e-governance services.
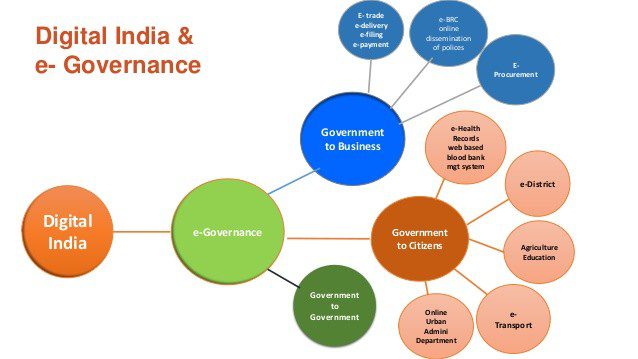
Examples of Successful E-Governance Projects
Several countries have successfully implemented e-governance initiatives:
Estonia:
Estonia’s e-residency program permits people around the world to set up and oversee businesses remotely, giving consistent advanced access to government services.
India:
The Digital India initiative aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society by providing digital administrations, bridging the digital partition, and promoting digital literacy.
Singapore:
The Shrewd Nation initiative coordinating digital technologies to improve citizens’ quality of life, enhance government administrations, and drive economic growth.
Data Security and Security Considerations
As e-governance involves the collection and processing of personal information, ensuring information privacy and security is paramount. Governments must receive robust data protection measures, follow international standards, and establish systems that safeguard citizens’ protection rights.
Future Trends in E-Governance
The future of e-governance holds exciting possibilities:
AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated processes will enhance citizen interactions, benefit conveyance, an administrative efficiency.
Blockchain’s decentralized and straightforward nature holds potential for secure and tamper-proof advanced trades, character confirmation, and record-keeping.
IoT gadgets can encourage information collection, checking, and benefit conveyance, making savvy cities and moving forward the quality of public services.
Conclusion
E-governance is transforming open administration, empowering governments to provide efficient, transparent, and citizen-centric services. By tackling computerized technologies, governments can enhance service delivery, promote transparency, and empower citizens. Be that as it may, tending to challenges
such as the digital divide, cybersecurity, and alter administration is vital for effective e-governance execution. As we grasp the computerized age, e-governance will proceed to advance, driving positive change in open administration.
FAQs
- How can citizens take advantage of e-governance?
E-governance benefits citizens by giving helpful get to to government administrations, advancing straightforwardness, improving benefit conveyance, enabling interest, and moving forward decision-making.
- What is the computerized divide?
The advanced partition alludes to the hole between people or communities who have get to to advanced advances, such as the web, and those who don’t . It can constrain the reach and effect of e-governance initiatives.
- How can governments guarantee information security in e-governance?
Governments can guarantee information security in e-governance by actualizing vigorous information security measures, following worldwide measures, getting educated assent, and building up clear arrangements on information taking care of and storage.
- What is the part of citizens in e-governance?
Citizens play a significant part in e-governance by effectively locking in government forms, giving input, taking an interest in decision-making, and utilizing e-services to get to government data and services.
- How will emerging technologies shape long-term e-governance?
Emerging advances such as AI, blockchain, and IoT hold the potential to revolutionize e-governance by improving robotization, security, and data-driven decision-making, driving to more proficient and successful open organization.