As concerns over climate change continue to grow, the use of solar energy as a renewable and sustainable source of power is becoming increasingly popular. One of the key components of solar energy systems is the solar panel, which converts sunlight into electricity. In recent years, advances in solar panel technology have led to the development of new materials that can help to improve the efficiency and durability of solar panels, as well as expand their potential applications.
One area where solar panels are seeing increased use is in roofing systems. Roof-mounted solar panels can help to reduce energy consumption and costs, as well as provide a source of clean energy. In order to ensure that these panels are as effective as possible, it is important to choose the right materials.
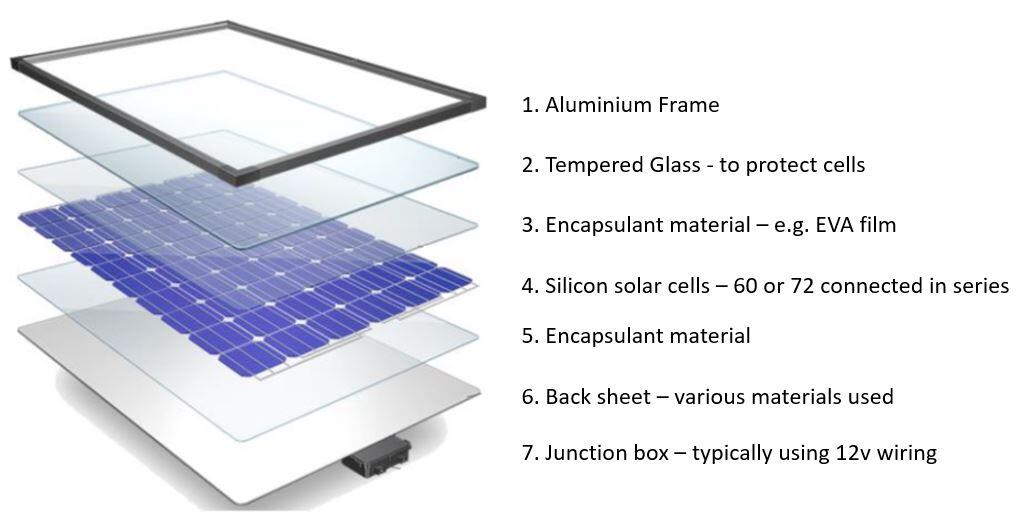
Material use in solar panel:
One type of material that is commonly used in roofing solar panels is silicon. Silicon is a semiconductor material that is able to convert sunlight into electricity through a process known as the photovoltaic effect. Silicon solar cells can be combined into modules and then installed onto a roofing system.
However, there are other materials that are being developed that can offer greater efficiency and durability than silicon. One example is perovskite, a material that is known for its ability to absorb light and convert it into electricity. Perovskite solar cells have the potential to be more efficient than silicon cells, while also being cheaper to produce.
Another material that is being explored for use in roofing solar panels is graphene. Graphene is a form of carbon that is extremely thin, lightweight, and flexible. It is also an excellent conductor of electricity and can be used to make solar cells that are both efficient and durable. Graphene solar cells have the potential to be thinner and more flexible than silicon cells, making them easier to install onto roofing systems.
In addition to these materials, there are also developments in coatings and surface treatments that can help to improve the performance of solar panels. For example, anti-reflective coatings can be applied to the surface of solar panels to help them absorb more sunlight. Meanwhile, hydrophobic coatings can help to repel water and prevent dirt and debris from building up on the surface of the panels.
Overall, the use of solar energy in roofing systems is an exciting area of development that has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about energy production and consumption. As advances in materials science continue to be made, we can expect to see solar panels become even more efficient, durable, and cost-effective. By investing in solar energy, we can help to create a cleaner, more sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.
Here are some key points on solar energy materials:
- Photovoltaic (PV) cells are the basic building blocks of solar panels. They convert sunlight into electricity.
- Solar panels can be made using different materials, such as silicon, cadmium telluride, and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS).
- Silicon is the most commonly used material in solar panels. It can be either monocrystalline or polycrystalline.
- Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is a thin-film material that is used in some solar panels. It is less expensive than silicon and has high efficiency.
- Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) is another thin-film material used in solar panels. It has higher efficiency than CdTe but is less widely used.
- Solar panels can be mounted on rooftops to generate electricity for homes or businesses. This is known as rooftop solar.
- Roofing solar panels can be integrated into the building’s design, providing a seamless look and saving space.
- Other solar energy materials include inverters, batteries, and charge controllers. These components work together to store and distribute the electricity generated by solar panels.
- Solar energy is a renewable and clean source of energy, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Research and development of new solar energy materials and technologies are ongoing to improve efficiency and reduce costs.