Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality refers to the integration of digital information and virtual objects into the absolute earth environment. By superimposing computer-generated comfort such as images, videos or 3D figures on top of the physical world, it boosts buyers to accept and collaborate with their climate Understanding the fundamentals of Augmented reality.
To understand the fundamentals of Augmented Reality (AR)
It’s critical to explore its key points, including its monitoring technology, imaging tools, and content creation. Tracking automation such as beacons, sensors or GPS enable Augmented Reality (AR) systems to understand the user’s location and direction. Display devices from smartphones to smart glasses provide decision while content creation includes the design and creation of virtual objects for the Augmented Reality (AR) action.
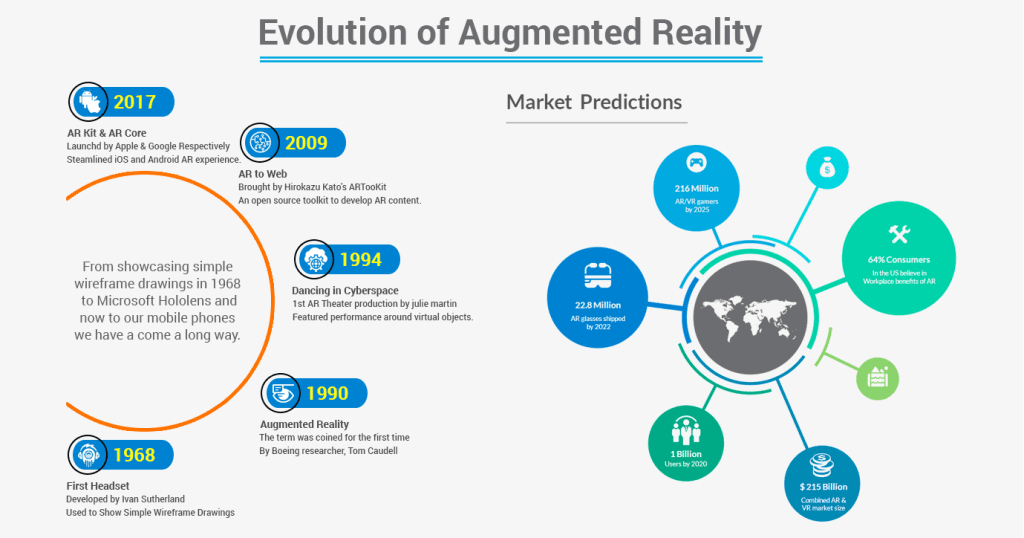
The evolution and development of the Augmented Reality:
AR has come a long way since its inception. At first it found application in military education and trade. However, as technology has enhanced AR has become more accessible to the accustomed public. The growth of mobile devices and the development of sophisticated AR platforms has acknowledged it to expand into many areas.
The Benefits and Uses of Augmented Reality:
The benefits of augmented reality extend to many industries.
AR administers better visualization, improved efficiency, increased commitment and enhanced customer experience. Sports and entertainment, retail and e-commerce, education and training, healthcare, architecture and design, etc. has function in the fields.
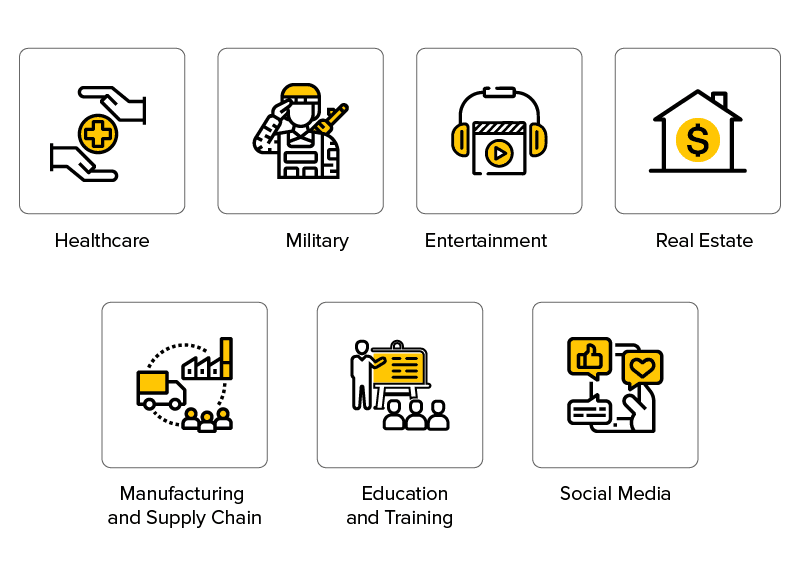
Augmented Reality in Various Industries
Augmented Reality in Gaming and Entertainment:
AR is refashioning the gaming and entertainment industry by combining the virtual and real worlds. It allows users to create a bilateral background by collaborating with virtual characters and objects in their physical climate.
Augmented Reality in Retail and E-Commerce:
AR is changing the retail and e-commerce landscape by conditional virtual experiences, product discussions, and enhanced objects in the world environment.
It bridges the gap between online and offline shopping, enabling customers to make informed decisions.
Augmented Reality in Education and Training:
AR has the potential to reconstruct education and training by providing interactive and experiential learning. It grants students to visualize complex concepts, explore virtual environments, and engage in hands-on action that deepen understanding and retention.
Augmented Reality in Healthcare:
The AR is making a big brunt in the healthcare industry, providing better analysis, surgical planning and clinical training. It helps doctors anticipate medical information, monitor it on the patient’s body, and advance certainty during surgery.
Augmented Reality in Architecture and Design:
AR is appealing to the architecture and design industry by allowing professionals to view and present virtual models of buildings or places in the real world. It facilitates better communication, association and accord making in the design process.
Overcoming the Challenges of the Augmented Reality Application While the
AR has many potentialities; its implementation comes with great challenges. These include management limitations, user adoption, privacy concerns, and the need for ability Overcoming these challenges requires critical thinking, continuous modernization and collaboration among many stakeholders.
Creating a Collaborative and Interactive AR Experience Knowing the full potentiality of AR should create a collaborative and interactive experience for users. This includes application of factors such as user interface design, virtual existence layout, communication and seamless integration with the physical environment.

Tools and Techniques for Augmented Reality Development:
Various tools and approaches are available for developing augmented reality applications. These range from AR development projects and libraries to drawing tools and 3D modeling software. Knowing these resources can help you build an appealing AR experience.
Best Practices for Content Creation:
To be fortunate in AR projects, it is big to follow best practices. These practices include user research, design for different devices and platforms, development providing clear feedback, and continuous testing and emphasis of AR experiences.
The Future of Augmented Reality:
With approach in hardware, software, and connectedness the future of augmented reality is promising. AR promises to be more logical and integrated in our daily lives. It will revolutionize many industries, enable new forms of human-computer interaction, and empower breakdown.
Conclusion:
Augmented Reality has the power to transform businesses, convert the user background and build new opportunities for innovation. By understanding AR’s principles, exploring its applications in assorted acreage and overcoming implementation challenges, businesses and individuals can tap into AR’s potential and live at the forefront of technological advancements.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions):
Q: How does Augmented Reality work?
A: Augmented reality build an decorated user experience by superimposing virtual content above the real world through monitoring technology and apparatus.
Q: What are the benefits of using truth in the marketplace?
A: Virtual reality in stores has benefits such as virtual testing, product analysis and customer advancement resulting in increased sales and customer satisfaction.
Q: Can virtual reality be used in education?
A: Yes, augmented reality has great potential in education. It supports interactive and experiential learning by permissive students to visualize complex concepts and achieve hands-on simulations.
Q: What are popular tools for creating virtual reality applications?
A: Some popular tools for architecture augmented reality apps include Unity, ARKit, ARCore, Vuforia, and Spark AR Studio.
Q: How is expanded reality good for the future?
A: Augmented reality will shape the future by becoming more seamless, everywhere and integrated into every aspect of our lives. It will change employment, transform the user background and enable new forms of human-computer interaction.